Summary
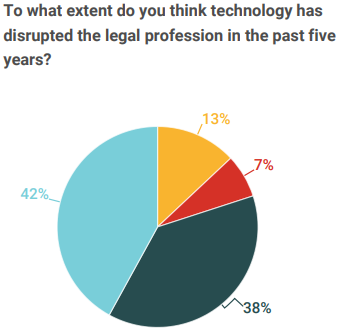
When asked if technology has been a disruptor in the legal profession in the last five years, survey results showed that only 7% answered to a great extent, with 42% stating to a small to a small extent, 38% to moderate extent and 13% not at all. Along with this, GCs also provided details on what tech is currently being used for within their departments and predictions for the future.
As the saying goes, "Ask a hundred lawyers and you'll get a hundred answers". Ask over a hundred lawyers about legal tech and the picture becomes even less clear. The legal tech ecosystem itself is so fragmented that almost no two GCs have the same thing in mind when talking about their use of technology.
Some companies are, to varying degrees of sophistication, implementing forms of automation or AI to solve legal or contractual issues, others are partnering with law firms to produce software capable of handling very specific issues like ISDAs, CLOs or loan documentation. But those applications of legal tech remain in the minority. Clearly, there is a distinction between legally useful technology and legal tech. Some basic elements of every office's software suite can be legally useful, though they are not generally badged as legal tech.
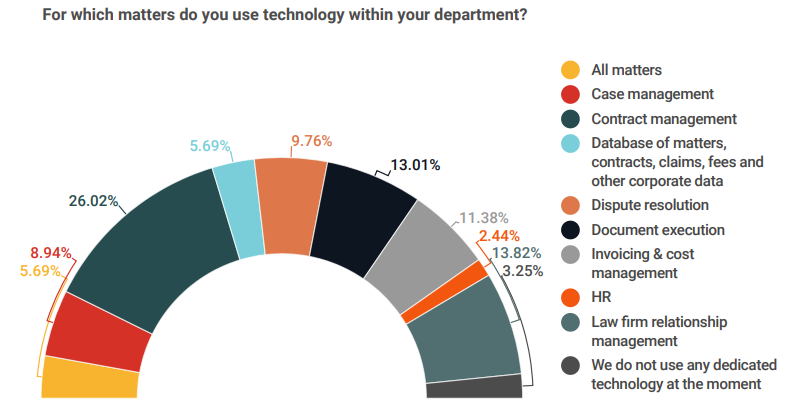
The results of our survey show that by far the most common use of legal tech, shared by nearly a third (32%) of teams, was contract management. However, the overall picture is one of a market still in its infancy. Respondents were as likely to use tech to manage relationships with their external firms (17%) or handle invoicing (14%) as they were to do automate legal advice.
Notably, these trends affected companies of all sizes: those employing more than 50,000 people and with legal teams with over 100 staff were no more likely to use advanced legal tech than small to medium sizes organisations. This should come as no surprise. Even companies that specialise in developing very sophisticated technology face the same issues as their less technologically advanced counterparts when it comes to finding solutions for the legal team.
As one respondent representing a Hong Kong-based tech and IT solutions company commented, 'As a provider of services then of course [the business] will have all this fancy technology, but most companies are much more sophisticated at developing things for clients than for themselves. As a user, as a GC using software to do something, you are in the same box as everybody else.'
Clearly, more money is invested in the revenue-generating side of a business than on its support functions. As experimental psychology has shown time and again, people naturally favour making gains over protecting losses, and businesses seem to be no different.
'Take a large bank,' continues our respondent. 'It may have well over 1,600 lawyers globally. That bank is effectively running a top 20 law firm in terms of its legal staff, and that's before you even consider its far larger compliance team. Yet when you look at how it is doing its legal work it will be nowhere near as sophisticated as a law firm. To understand why that should be the case you've got to consider that the law firm is practicing law as a business whereas the in-house counsel is a cost. Anything that solves a problem for in-house counsel therefore needs to be quantified as a cost saving when proposed to the business, which makes it much harder to justify.'
'Even the most persuasive pitch for new legal technologies looks unappealing to most businesses because all you're doing is comparing one cost with another cost: the cost of technology vs the cost of salaries to do the same job. Either way you're reinforcing the view that you are a drag on the business that will incur costs! It's not at all true - those are jobs that need to be done, but it's how people will see it.'
Innate risk aversion when it comes to corporate budgeting is only part of the story, however. Part of the answer to why GCs struggle to acquire technology lies within the legal team itself. First, lawyers tend to be poor at understanding and explaining their technology needs. They may understand their legal needs very well, but this does not necessarily translate into seeing what sorts of tools they need to accomplish that end.
As another respondent pointed out, it also requires a lot of time and no small amount of skill to adequately benchmark legal tech. 'Even doing the work to see whether an automatic translation service for legal documentation is efficient if automated and whether that can be measured in terms of efficiency gains is not something I would expect many GCs to successfully handle. Lawyers are generally terrible at that sort of exercise, which is a procurement exercise we are just not trained in.'
But - and this is neither the first nor last time this will be said about the subject of legal tech - a change may be about to come.
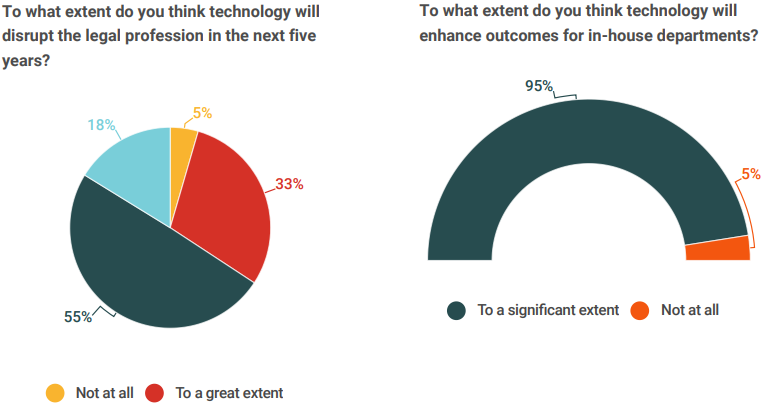
Over two thirds (68%) of those surveyed said that the use of technology within the legal team had increased significantly over the past five years. Just 5% reported that their use of technology had not increased at all. The bulk (95%) of respondents though that legal tech would end up significantly enhancing the day-today operations of the legal team, while nearly three quarters (73%) said they would like to step up their use of technology.
Perhaps a clearer indication of this change is that, for all their cynicism over tech, GCs are not disputing that it has changed the profession - 87% of respondents said that legal tech had already changed the industry to at least some extent. Even more strikingly, 95% of GCs felt legal tech would change the industry in the coming years, with 33% saying that the change would be significant.